ARNOWA for Smart Local Governments
INTRODUCTION
Smart cities are frequently seen as groups of instruments across many scales that are linked through numerous systems. These systems deliver uninterrupted data regarding the actions of people and materials in terms of the flow of decisions about the physical and communal form of the city. Cities however can only be smart if there are intelligence functions that can incorporate and synthesise this data to some purpose, ways of enhancing the efficiency, equity, sustainability and quality of life in cities.[rml_read_more]
In the last few decades, the concept of smart city has become very popular in scientific literature and international policies. This popularity could be accredited to the footing that the smart city concept has achieved as a vision for enhancing the economy, mobility, environment, people, living standards, and governance of cities. The recent abundance of big data has contributed to smart city transformation.

“Big data” refers to enormous intricate sets of data that characterize digital traces of human activities and can be defined in terms of scale or volume, analysis methods or effect on organizations. Cities, globally, collect vast quantities of data associated to urban living from objects (e.g., energy infrastructure) and stakeholders (e.g., energy-using residents). Use of these data impacts the creation of useful content for various stakeholders, including inhabitants, tourists, local government, and businesses.
APPLICATION AREAS FOR LOCAL GOVERNMENT
Local operations management relies on data from local service providers, such as city infrastructure, environmental, and company resource data. Local governments have the capacity to improve their operational processes with the help of enhanced communication within processes (between resources, infrastructure, and citizens or visitors) using data .Smart technology can be applied by local government in various sectors of the city to improve their management and efficiency and hence lead towards a sustainable future.
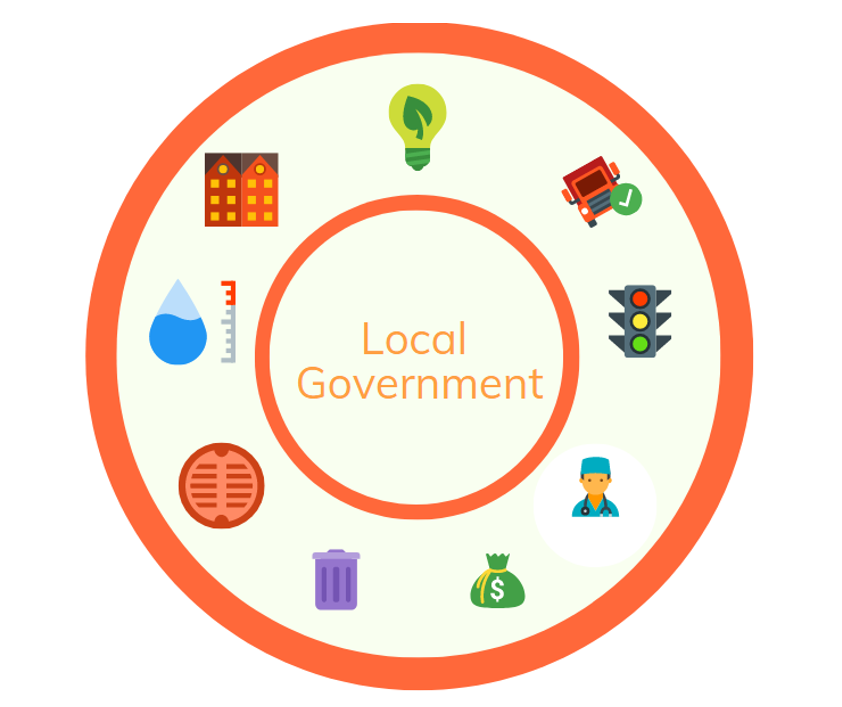

Some of the application areas include:
- Smart Energy
- Smart Water and Wastewater Management
- Smart Health Management
- City Waste Management
- Environmental Pollution Management
- Smart Transportation
- Smart Building Management
- Public Space Management
Smart Energy
While cities present specific energy and environmental challenges, urban density, in the words of the C40 Cities Climate Leadership Group, can create the likelihood for an improved quality of life and a reduced carbon footprint through proficient infrastructure and planning.
Application of smart technology is beneficial for the local government in terms of increasing the energy efficiency and reducing electricity consumption throughout the city. Few benefits of applying the smart concept include predicting and mitigating losses, controlling peak demand, and mechanical fault location, isolation, & service remodelling.
This impact on supply reliability, losses, and voltage administration, while algorithms also calculate the best configurations possible on the basis of the data that is collated from smart devices such as smart sensors, meters, and a plethora of switch operations. Utilising this technology provides many advantages, such as diminished losses, improved voltage quality, and the enablement of an optimal voltage profile.
The data from these smart devices grants for the formation of an optimization model that permits the optimal planning and operation of energy resources within the city such that synergies between systems can be identified and properly assessed. This can help the concerned authorities in the assessment of the profitability of the considered systems, assisting them in their implementation.
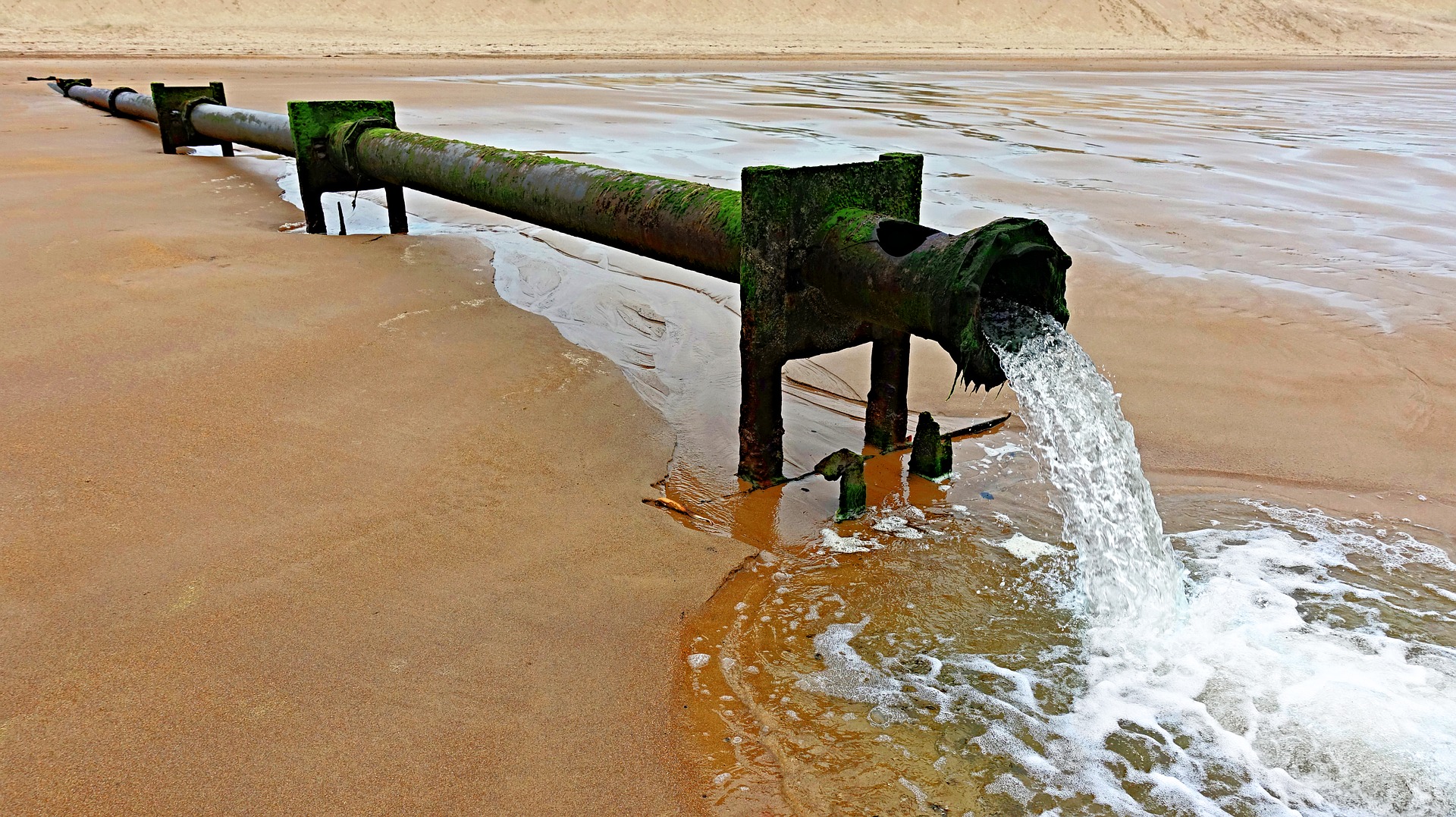
Smart Water and Wastewater Management
According to the UN, almost half of the world population will face water scarcity by 2025 which clearly indicates that water will be a valuable resource in near future. Water Management System is highly impacted by smart technology. It is challenging to ensure the proper utilization of water, but proper implementation of smart technology in Water Management Systems can surely make it convenient for local governments to manage and conserve our valuable resources.
Water conservation is one of the crucial aspects in water management, especially in cities, where maintaining a record of water consumption is an enormous task. This issue can be solved using smart technology which through real time data collection and analysis keeps record water consumption by the citizens. The collected data can be analysed to determine the amount of water consumed by the people in the city on that particular day. This helps the local government manage the flow of water in much more effective manner.
Similarly, monitoring wastewater levels, leakages, water quality and water flow through different channels is a major challenge for the water authorities. Smart devices detect the temperature changes, water leakage, chemical leakage, and pressure levels, collect the information and send it to the managing authorities. This ensures that any issues occurring can be resolved quickly and also help detect and calculate the amount of chemical residue present in the water.
Smart technology also allows the local government to make irrigation of common city areas smart. At present, a huge amount of water gets wasted during the irrigation process as it is scheduled automatically at particular times of the day regardless of the weather conditions and moisture present in the soil. Smart technology overcomes this problem by collecting the data on the weather condition and the soil moisture and transferring it to the local authorities who can then supply water to the irrigation systems based on the desired quantity at the desired time
The collected data, overall, allows the local governments to manage irrigation of common areas, water supply requirements, wastewater management and water conservation. Moreover, the captured data allows for real-time analysis of water testing and helps obtain information like Total Dissolved Solids (TDS), Bacteria, Chlorine, Electrical conductivity, etc. This helps in accessing the real-time, accurate quantification of results and provides the authorities with the ability to pinpoint the problem areas thereby making management simple.
Smart Health
World Health Organization claims that more than 5.5 million people lose their lives annually to the rising levels of air pollutions, so increased visibility into pollution levels through smart technology can create timelier and more precise warnings that can help save lives. They are also helpful in addressing health concerns for the citizens that have breathing problems such as asthma. On a smaller scale, the collected data from the deployed smart devices can be used by the local government for city decision-making. For example, data on noise levels might lead to a decision on where to build a school.
Smart Technology in healthcare can provide a wider prospective of the citizens’ wellbeing. It is similar to enabling a patient to undergo a diagnosis well before the start of the treatment. In fact, its usage goes beyond the “diagnosis” stage.
The huge amount of data collected allows the local authorities to develop service planning that will make public health their prime priority. Furthermore, the medical data can be kept undisclosed to keep the citizens’ sensitive information private and confidential and hence not violate their privacy rights. Moreover, the accumulated medical data can be utilized to foster innovation and enhance cooperation which will benefit the city’s healthcare system. If the data is made available by the local authorities while maintaining the inhabitants’ discretion, enhancements and improvements can be made in the city’s healthcare system and hence contribute positively towards maintaining a good and sustainable quality of life.
City Waste Management
Smart technology can have a huge impact on the waste management system of a city. Application of IoT and smart devices provide real time data to the concerned department of the local government who can then take the required action in time. With smart technology applied to the bins spread out through the city, waste management becomes a menial task. The data collected from these installed waste containers gives information on their fullness levels and weight in real-time. Smart technology allows local authorities to access this data anywhere anytime. This allows them to manage and optimize waste collection dates, thus, dispersing the collection trucks only when it is required instead of the fixed routinely visits irrespective of whether it is needed or not.
This lets the authorities to eliminate costs and risks associated with unnecessary collection, including fuel, staff time and maintenance costs and at the same time maintain sanitation around the city. Emptying only full trash cans allows them to thereby streamline their service and save big. It can also provide them with opportunities to resize the collection workforce based on the patterns drawn on the context of the received data.
Furthermore, the fossil fuels needed to power the collection trucks and their emissions cause great harm to the environment. Incorporation of smart technology into waste management systems is expected to reduce this harm by up to 50% thereby contributing towards a sustainable environment.
Smart Transportation
Smart public transport technology can help local governments to make the cities function more efficiently while upgrading services to citizens. Hazardous weather conditions, intense traffic, and risky speeds can all result in accidents and fatalities. Smart technologies have the ability to improve commutes across traditional public transport, with immediate benefits for city dwellers across the globe. The data collected through the deployed smart technology can aid the local authorities to control traffic, limit infrastructure damage, making public parking spaces more efficient and enhance traffic safety.
Real-time weather monitoring systems associate data on wind speed, visibility, road conditions, and rainfall, providing traffic controller on information on up-to-date driving conditions. These smart transportation systems enable traffic lights to respond based on the changing traffic patterns instead of a fixed schedule. This allows for prioritizing certain traffic, such as public transit and emergency vehicles. Collecting traffic data also helps measure peak traffic times; journey distances and other data that help optimize the traffic situation in the city.
Data collection also makes parking management a breeze. Smart parking systems scan the vehicles for their number plates, available parking spaces in the lot and transmit this information to reduce parking time. This also helps to document illegally parked vehicles thereby making it easier to enforce parking regulations throughout the city streets.
Smart Building Management
Smart technology can be implied in the form of “Building Utility Management Systems” or “BUMS” which entails of centralized systems that monitor, control, and record the functions of building services systems. BUMS works by linking the functionality of individual equipment and operate them as one integrated system. The features of a smart BUMS have been depicted in the infographic below-
With the rising electricity costs and energy consumption by buildings, it is essential for local governments to optimize the public building operations to tame these expenditures and improve their consumption patterns based on the occupancy levels, weather conditions, and time of day and routine patterns. Smart technology not only integrates all the elements of the building but also provides real-time data to the concerned authorities to facilitate the management of the entire building while at the same time enhance the operations of the employees by providing the correct working conditions and HVAC. Smart technology also helps to enhance the overall physical of the building through smart video analytics.
Since through application of smart technology the building functions operate in the ‘cloud’, such as cloud-based analytics, and the ability to access and manage multiple buildings remotely it becomes easier for local authorities to manage all concerned buildings at the same time without any hassle. The ability to access live analytics or receive alarm notifications from hand-held devices makes managing these buildings even simpler.
Public Space Management
Public space plays an important role in the city’s inclusive development and hence is a central topic when it comes to urban planning circles by the local policy makers. Smart technology has the ability to transform the conventional user experience and enhance the capacity of public spaces to accommodate the present day lifestyle of the citizens Monitoring of public spaces through the application of smart technology helps improve accessibility, utilization or aesthetics of public spaces, and also helps the authorities in understanding the behavioural patterns of the citizens through collection of dynamic data (pedestrians, mobility behaviour, environmental data, etc.).
The incentive for this data-gathering is to assist local governments in decision-making. Continuous assessment can serve as a basis for the further development of urban public spaces, in terms of fulfilling the requirements of the city residents and increasing the attraction of public spaces.
ARNOWA FOR LOCAL GOVERNMENTS
ARNOWA provides smart solutions for all the aforementioned areas. ARNOWA is a smart real-time data acquisition, analytics, reporting, verification, and management system. Combined with artificial and real intelligence, ARNOWA supports proactive monitoring, converting data to knowledge, predicting issues, periodic reporting, advising improvements, alarming and making informed decisions. It involves a human interface, which provides proficient analysis of the information and knowledge stimulated out of the monitored data and converts it into wisdom that can be used for efficient decision making, improving the present as well as the future. ARNOWA facilitates audit needs and improves management by providing transparency, accuracy, and useful advice.
ARNOWA not only monitors and records data, but also provide a series of existing problems, diagnose the inefficient points, and provides solution to maintain efficiency levels through timely reporting and continuous support.
Sensors:
- Temp & Humidity
- Probe Thermocouple
- Light Intensity
- Motion Sensor
- People Counter
- Mobile Beacons / Counters
- Vibration Sensor
- Noise Sensor
- Pressure Sensor
- GPS
- Air Quality Sensor
- Dust Sensor
- Weight Sensor
- Touch Sensor
- Weather Station
- Water Quality (Ion /TDS, DO, pH)
- Heart Rate / Pulse Sensor + Body Temp
- Ultrasonic distance for bins
- Soil Moisture Probe
Meters:
- Electric
- Water
- Gas
- Meter Extenders: KNX, BACnet, Modbus to Wi-Fi, LORA
Smart Pole:
Lights (Modulated LEDs), Sensors, Comms and Advertising
CCTV:
With advance video analytics and machine vision artificial intelligence functionality
REFERENCES
- Batty, M., Axhausen, K., Giannotti, F., Pozdnoukhov, A., Bazzani, A., Wachowicz, M., Ouzounis, G. and Portugali, Y. (2012). Smart cities of the future. The European Physical Journal Special Topics, 214(1), pp.481-518.
- Lim, C., Kim, K. and Maglio, P. (2018). Smart cities with big data: Reference models, challenges, and considerations. Cities, 82, pp.86-99.
- Lo, C. and Lo, C. (2019). Smart cities: redefining urban energy. [online] Power Technology | Energy News and Market Analysis. Available at: https://www.power-technology.com/features/smart-cities-redefining-urban-energy/ [Accessed 26 Dec. 2019].
- Schneider Electric Blog. (2019). How smart technology is leading the way for Energy Efficiency in Electric Utilities – Schneider Electric Blog. [online] Available at: https://blog.se.com/energy-management-energy-efficiency/2018/07/04/smart-technology-leads-the-way-for-energy-efficiency-at-electric-utilities/ [Accessed 26 Dec. 2019].
- Francisco, C. and Munoz, C. (2017). Energy Management in Smart Cities. KTH Royal Institute of Technology.
- A, Q., Feed, M. and America, U. (2019). How can IoT help in Water Management System?. [online] Smart Water Magazine. Available at: https://smartwatermagazine.com/blogs/parija-rangnekar/how-can-iot-help-water-management-system [Accessed 24 Dec. 2019].
- Lo, C. and Lo, C. (2019). Smart cities: redefining urban energy. [online] Power Technology | Energy News and Market Analysis. Available at: https://www.power-technology.com/features/smart-cities-redefining-urban-energy/ [Accessed 26 Dec. 2019].
- Smart City. (2019). How Use of Sensor Technology Overcome Challenges in Health Sector?. [online] Available at: https://www.smartcity.press/sensor-technology-for-public-health/ [Accessed 26 Dec. 2019].
- here.com. (2019). Smart Transportation: Benefits And Real Life Examples | HERE Mobility. [online] Available at: https://mobility.here.com/smart-transportation-benefits-and-real-life-examples [Accessed 26 Dec. 2019].
- Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft | Morgenstadt. (2019). Connected public spaces. [online] Available at: https://www.morgenstadt.de/en/innovation_areas/connected_public_spaces.html [Accessed 26 Dec. 2019].




